Gallery¶
Here we provide a gallery containing selected example results of several applications (a non-exhaustive list) using SPUX framework for Bayesian inference and uncertainty quantification.
Randomwalk¶
A simple one-dimensional randomwalk with uncertain origin, drift, and the observation error.
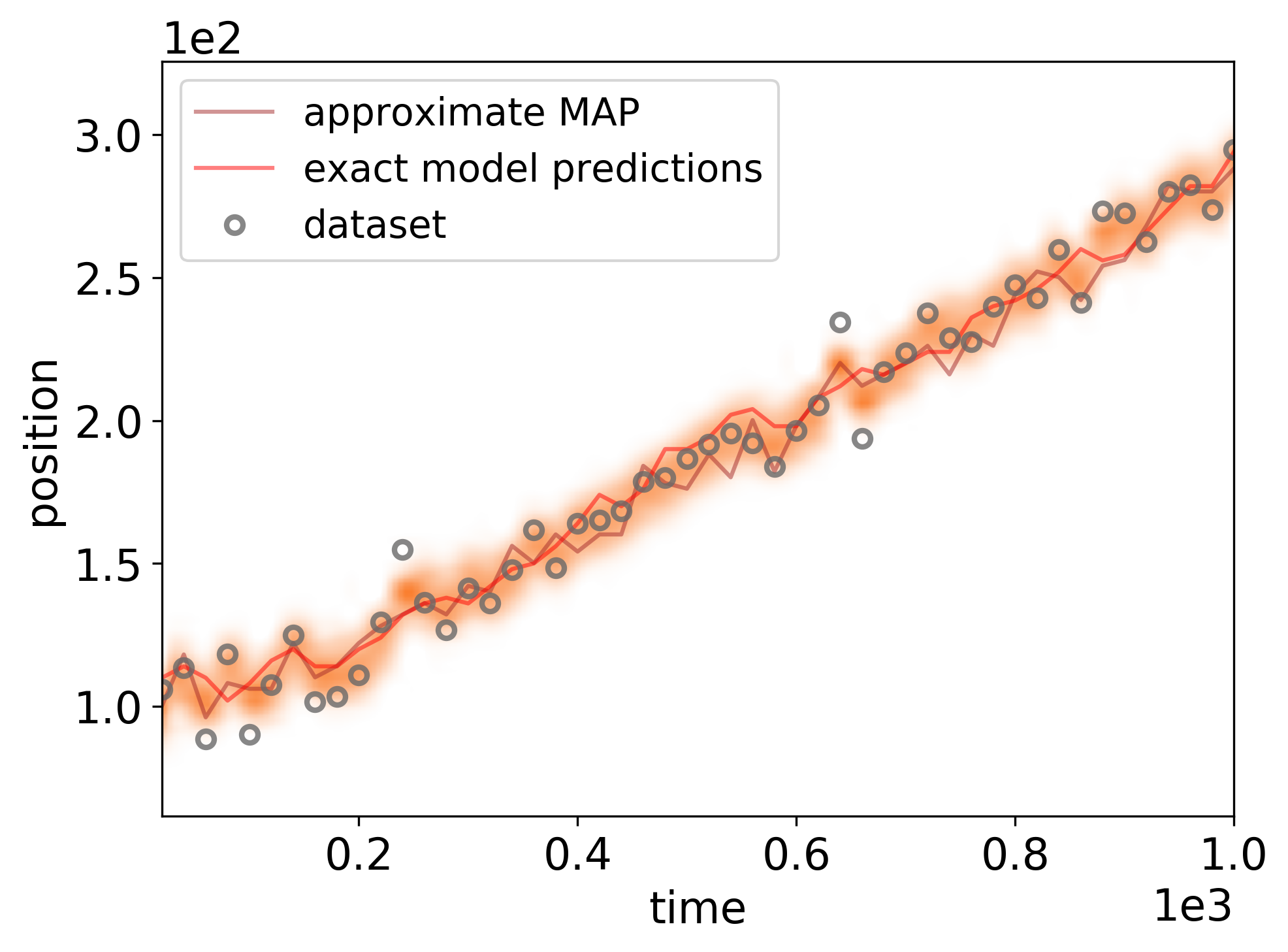
Posterior distribution of model predictions for the observational dataset. The shaded orange regions indicate the log-density of the posterior model predictions distribution at the respective time points, the brown line indicates the approximate MAP model prediction., the red line represents the exact model prediction values.
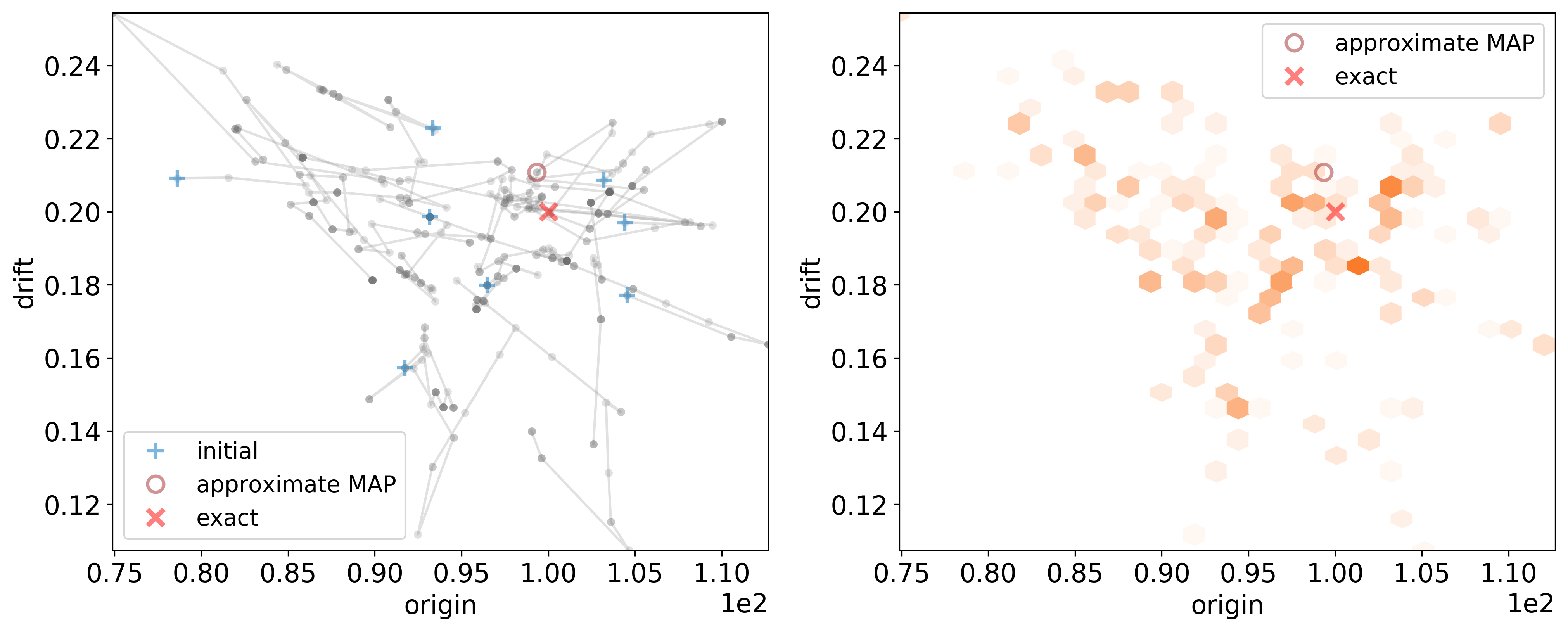
Joint pairwise marginal posterior distribution of origin and drift, including the corresponding Markov chains from the sampler. Legend: thin semi-transparent gray lines and dots - concurrent chains, orange hexagons - histogram of the joint pairwise marginal posterior parameters samples, blue “+” - initial parameters, brown “o” - approximate MAP parameters, red “x” - the exact parameters.
Linear bucket¶
rpy2 bindings to Python.Work in progress.
Stochastic inputs¶
numba compiled C code for computationally expensive parts.Publication: Del Giudice, D. et al., (2016) “Describing the catchment-averaged precipitation as a stochastic process improves parameter and input estimation; Water Resources Research. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 52(4), pp. 3162–3186. doi: 10.1002/2015WR017871.
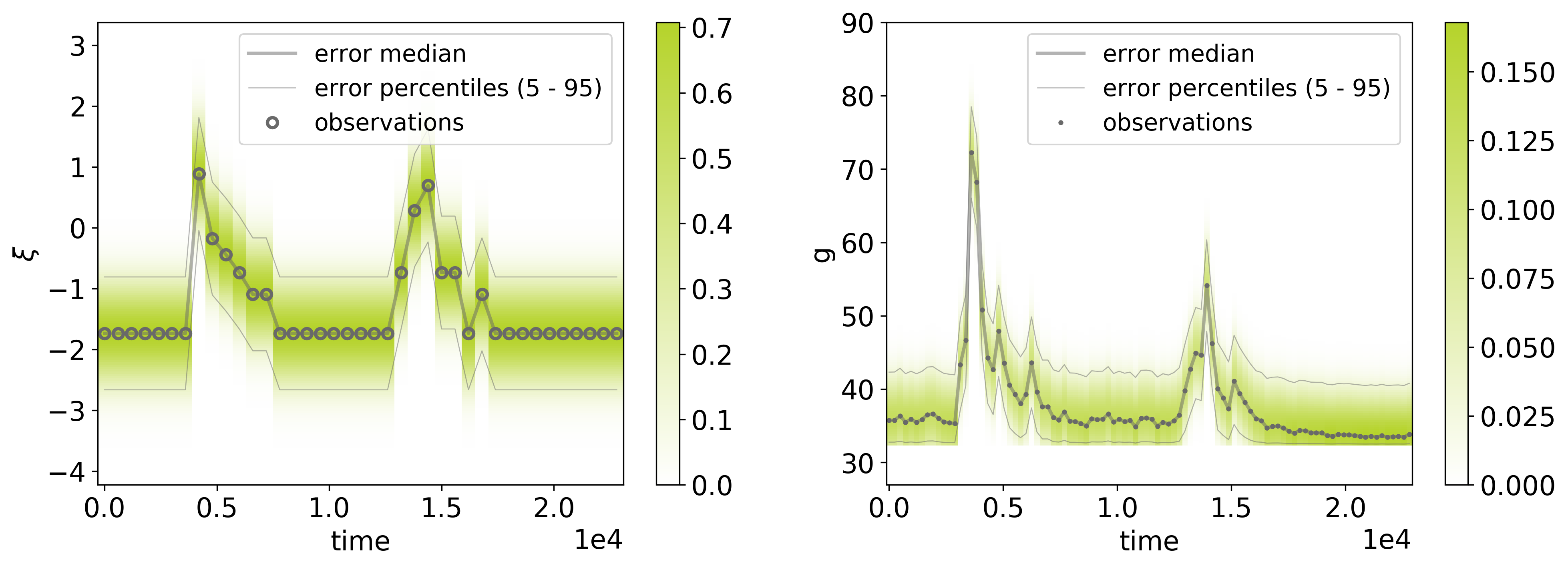
The first dataset and the associated heteroscedastic error model for the input (precipitation) and the output (discharge) measurements.
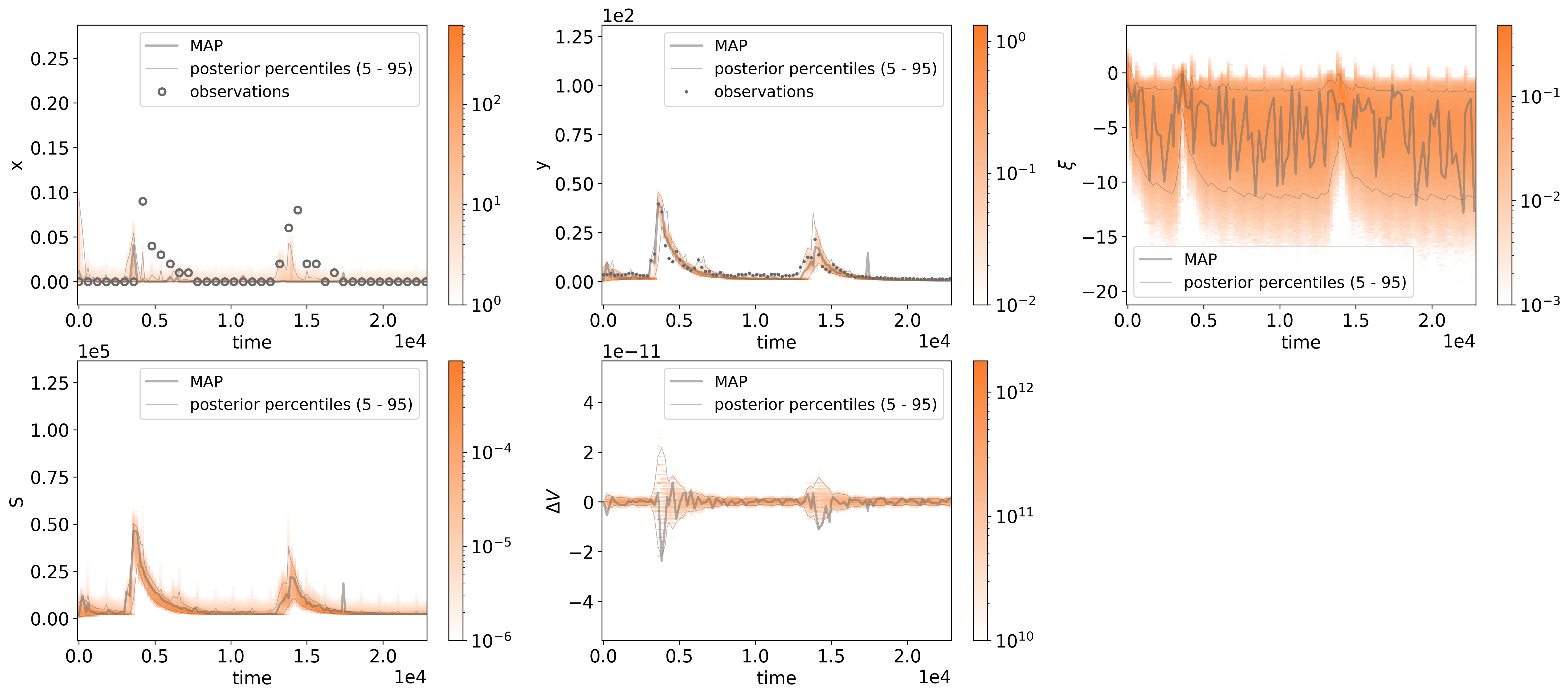
Plots of the posterior distribution of model predictions for an observational dataset above,
including auxiliary posterior distributions for rainfall potential $\xi$, reservoir level S, and the water volume discrepancy $\Delta V$.
Work in progress.
Stochastic parameters¶
ctypes bindings of the compiled Fortran model library to Python.Work in progress.
Prey-Predator¶
JPype bindings to Python.Publication (preprint available at http://arxiv.org/abs/1711.01410):
Šukys, J. and Kattwinkel, M.
"SPUX: Scalable Particle Markov Chain Monte Carlo
for uncertainty quantification in stochastic ecological models".
Advances in Parallel Computing - Parallel Computing is Everywhere,
IOS Press, (32), pp. 159–168, 2018.
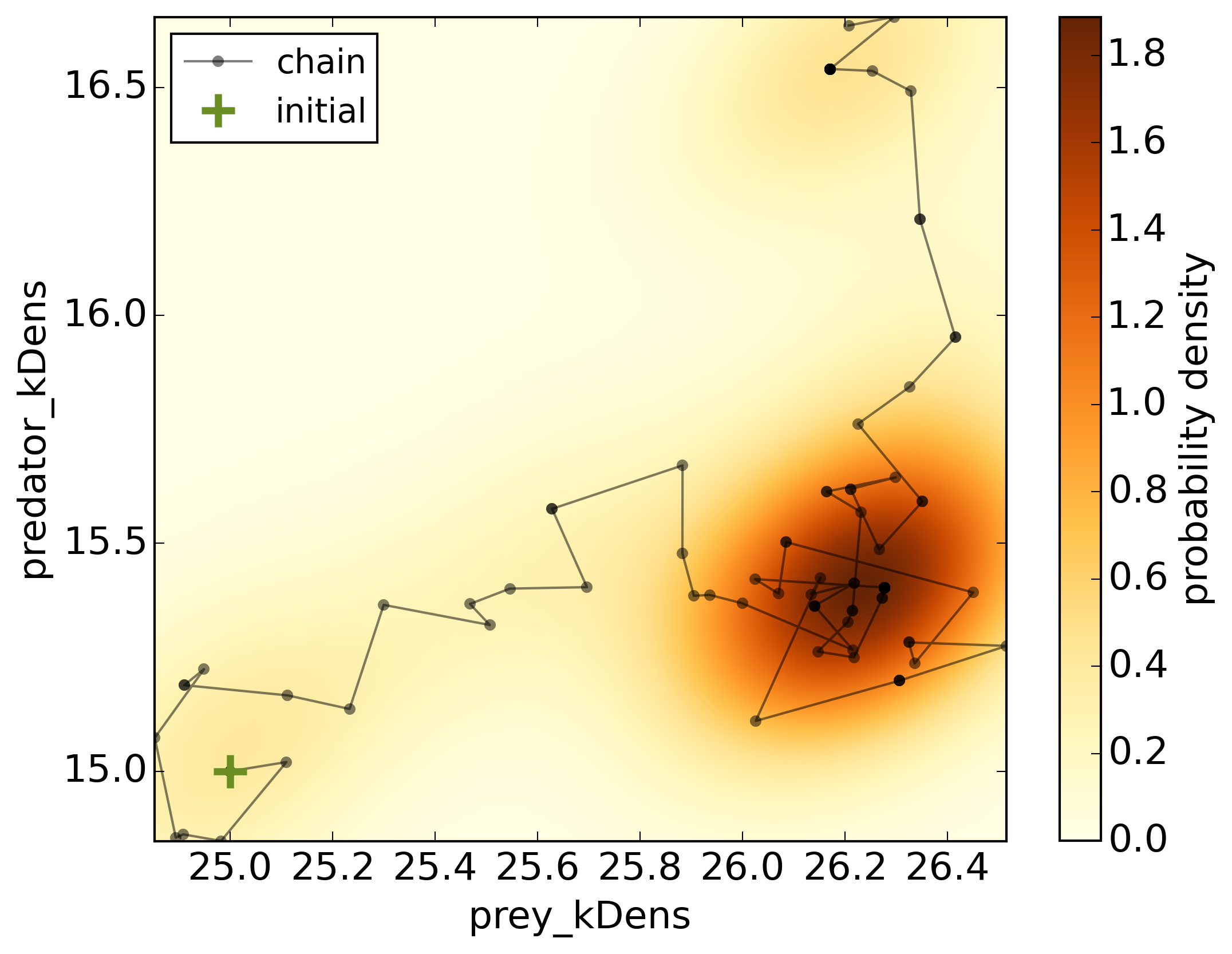
Marginal posterior distribution of prey_kDens and predator_kDens parameters,
including the corresponding MCMC chain from the sampler.
Legend:
green “+” - initial parameters.
Work in progress.
River invertebrates¶
JPype bindings to Python.Work in progress.
DATALAKES¶
ctypes bindings of the compiled Fortran model library to Python.Work in progress.
In-stream herbicides¶
ctypes bindings of the compiled Fortran model library to Python.Work in progress.
Urban hydrology¶
Swig wrapper for Python.Work in progress.
Solar dynamo¶
BISTOM - calibration of the solar dynamo simulations.
Work in progress.
